
New Blood Analyzer Tells Human from Animal Samples on the Spot
The system could someday provide fast results at a crime scene

The system could someday provide fast results at a crime scene
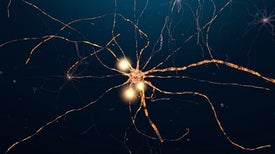
Optogenetics could aid vision, blood glucose, and more
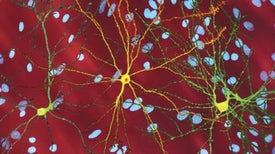
Hopes were high for drugs designed to lower levels of a mutant protein, but development has stalled

Next-generation COVID-19 vaccines will not only tackle different versions of the virus but will provide solutions across the world at a fraction of the cost

Organoids made of tear-producing cells offer chances to study, and possibly treat, eye disorders

Researchers are training algorithms to emulate trained dogs’ ability to detect cancer and other diseases, perhaps including COVID-19
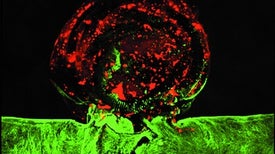
Scientists make and treat a 3-D-printed model of a ballooning blood vessel

Scientific American and the World Economic Forum sifted through more than 75 nominations for the most innovative and potentially game-changing technologies in 2020. The final top 10 span the fields of medicine, engineering, environmental sciences and chemistry. And to win the nod, the technologies must have the potential to spur progress in societies and economies by outperforming established ways of doing things...

A radical procedure restores touch and grasping in former amputees

An experiment stimulates monkeys’ brain to generate shape perceptions
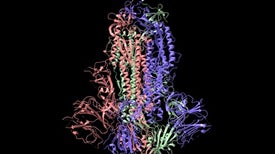
Google’s deep-learning program for determining the 3-D shapes of proteins stands to transform biology, scientists say

Bacterial breathing helps to build a futuristic “2-D” semiconductor

A big advance in synthetic biology

Therapeutic and diagnostic apps and bots are almost here

Fewer trips to medical labs make care more accessible

An article in Nature lays out 10 bold predictions for a field whose extraordinary achievements are just the beginning of what could be possible

Scientific American’s senior medicine editor Josh Fischman talks about issues in medicine and public health that will be affected by this election.

New models used writing samples to predict the onset of the disease with 70 percent accuracy
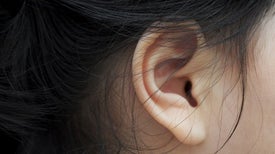
A noninvasive device designed to rewire brain circuits reduced symptoms of tinnitus in a large, exploratory clinical trial

In vivo bioprinting might also help repair hernias and treat infertility
Support science journalism.

Thanks for reading Scientific American. Knowledge awaits.
Already a subscriber? Sign in.
Thanks for reading Scientific American. Create your free account or Sign in to continue.
Create Account